The gears of high-viscosity pumps commonly include straight teeth, helical teeth, herringbone teeth, and helical teeth. The tooth profiles are mainly involute and arc types. The width of the teeth of SS high-viscosity pumps used in high-pressure applications is smaller than the diameter of the addendum circle. This is to reduce the radial pressure area of the gear and reduce the load on the gear and bearing. Because the medium delivered by the SS high-viscosity pump has a high viscosity, in order to reduce the movement resistance and improve the pump's liquid absorption capacity, the medium must be heated or insulated. Electric heating elements are usually used to heat the viscous liquid evenly. If the temperature fluctuates little and the high-viscosity liquid being transported is prone to degradation, it is recommended to use the fluid heating method, especially the high-viscosity gear oil pump with large displacement. Fluid heating is divided into internal and external structures. The so-called built-in type refers to the design of a heat-protruding jacket inside the pump body or end cover of the SS high-viscosity gear oil pump, and the external type is to connect the heat jacket with the pump body through bolts. The steam and heat transfer oil are still used as cooling water into the jacket, which depends on the details of the medium. The built-in type is suitable for the occasions where the average temperature of the conveyed liquid is required, or the average cooling of the high-temperature liquid is required. When the electric heating method is lacking or the temperature control requirement is not high, an external structure can also be used. The jacket of the pump head department can control the temperature of the conveying fluid, whether it is in a high temperature or low temperature environment, it can be equipped with an external jacket.
Because the medium delivered by the high-viscosity gear oil pumps has a high viscosity, in order to reduce the movement resistance and improve the pump's liquid absorption capacity, the medium must be heated or insulated. Electric heating elements are usually used to heat the viscous liquid evenly. If the temperature fluctuates little and the high-viscosity liquid being transported is prone to degradation, it is recommended to use the fluid heating method, especially the SS high viscosity gear oil pumps with large displacement. The fluid heating is divided into internal and external structure. The so-called built-in type refers to the design of a heat-protruding jacket inside the pump body or end cover of the stainless steel high-viscosity gear oil pump, and the external type is to connect the heat jacket with the pump body through bolts.
High-temperature and stainless steel high-viscosity pumps often use displacement gears, and melt pumps that convey high-viscosity and high-pressure polymer melts mostly use involute helical gears. The gear and the shaft are made into one body, and its rigidity and reliability are higher than that of a high-viscosity pump manufactured separately from the gear and shaft. The gears of foreign low-pressure and high-viscosity pumps often adopt a square structure, that is, the tooth width of the gear is the diameter of the addendum circle.
Generally, small high-viscosity pumps use involute spur gears, high-viscosity pumps often use displacement gears, and involute helical gears are used for melt pumps that transport high-viscosity and high-pressure polymer melts. The gear and the shaft are made into one body, and its rigidity and reliability are higher than that of a high-viscosity pump manufactured separately from the gear and shaft. The gears of foreign low-pressure and high-viscosity pumps often adopt a square structure, that is, the tooth width of the gear is equal to the diameter of the addendum circle.
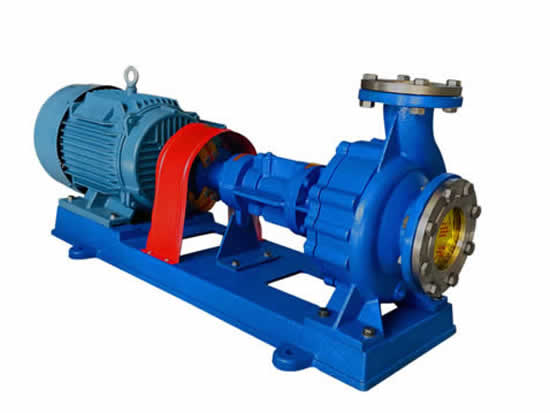
The heavier the pump casing of a high-viscosity pump, the higher its temperature and pressure resistance. The pump body is usually made of ductile iron, or it can be made of forged aluminum alloy hard die casting, or it can be manufactured by using extruded aluminum alloy profiles. When the conveyed medium is corrosive, stainless steel with higher cost can be used. Foreign high-viscosity pumps mostly use nickel-containing and high-chromium alloy steel as the pump casing material. This material has better comprehensive functions in terms of strength, reliability and cost. In order to solve the problem of oil trapping in high-viscosity pumps, symmetrical unloading grooves are usually opened on the pump cover, or divergent unloading grooves are opened in the direction of the low pressure side. The suction side uses a tapered unloading groove, and the discharge side is rectangular. The depth of the unloading groove is also deeper than that of the high-viscosity pumps used in the hydraulic industry.






 +8617731766260/18233754501
+8617731766260/18233754501  fan@saikenpumps.com
fan@saikenpumps.com






 +8617731766260/18233754501
+8617731766260/18233754501 +86-317-8227664
+86-317-8227664
 +8618233754501
+8618233754501