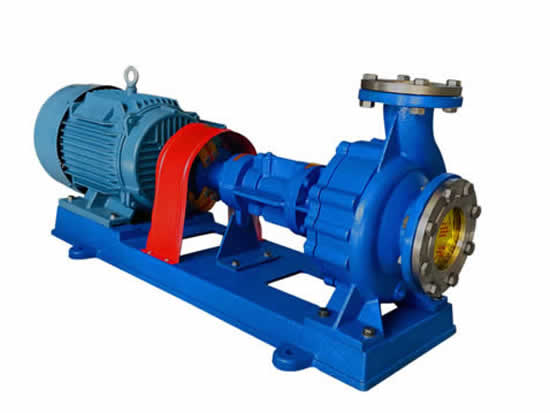
Operation and maintenance of gear pumps
Gear pumps are the most common positive displacement pumps for transporting high viscosity fluids such as automotive oil, plastics, paint, adhesives and soap. They operate by generating suction at the entrance. They have two rotating components of gears - drive gears and inert wheels. The pump flow rate is determined by the cavity (volume) between the gear teeth, the sliding amount (reverse flow) and the gear rotation speed (rpm).
Like any pump, proper operation and regular maintenance are essential to reduce costly pump maintenance and maximize pump efficiency. The following are useful tips for operating gear pumps and ensure long service life through regular maintenance.
Gear pump operation
- near maximum rated speed operation. Because gear pumps & KCB gear pump have poor volumetric efficiency at low speed and low flow rate, they should run as close as possible to their maximum rated speed in order to improve production and efficiency.
- use special materials when using abrasive to pump liquid. The gear structure of the gear pump allows particles to be trapped in a narrow space to accelerate wear and reduce efficiency. If you need to transport fluid containing abrasives, consider contacting the pump manufacturer to discuss hardening material options.
Ensure that the total life span is less than 8.0 PSI. Gear pumps do not produce perfect vacuum, requiring total lift (including pipeline friction loss) to be half of atmospheric pressure (about 8.0 PSI).
- avoid low viscosity fluids. Gear pumps (especially NYP internal gear pump) are designed to handle high viscosity fluids to minimize sliding. Pumping low viscosity fluids results in reduced velocity and efficiency because it "slides" through the narrow space from the high-pressure discharge side of the pump to the low-pressure suction side of the pump.
Do not dry. Unlubricated gear teeth will friction together, generating friction and heat when the gear expands and begins to friction the housing. This will damage the pump and require expensive maintenance and downtime.
Gear pump maintenance
- maintain maintenance records. One of the most important measures you can take is to ensure that your pump runs smoothly. This is a detailed record of maintaining the performance of the baseline pump, regular maintenance and any maintenance. This will help you determine how the pump will operate in the future and the best way to repair or replace specific components.
Check bearings regularly. Bearings are the most important maintenance area of gear pumps, because if they are misaligned or defective, they can lead to imbalance. Check bearings regularly and remove defective bearings with puller when necessary. Excessive noise may be an indicator of bearing wear.
Check gear pump clearance. The new gear pump has a clearance of 0.009 to 0.007 inches with the teeth and cavity of the gear. Try to pass a piece of paper between the gaps and check the wear of the teeth regularly. If it is easy to pass through the gap, it indicates that the bearing has been worn and should be replaced.
By following the regular maintenance plan and following the correct operating procedures, gear pumps can be an efficient and efficient solution for high viscosity pumping requirements.





 +8617731766260/18233754501
+8617731766260/18233754501  fan@saikenpumps.com
fan@saikenpumps.com






 +8617731766260/18233754501
+8617731766260/18233754501 +86-317-8227664
+86-317-8227664
 +8618233754501
+8618233754501